Difference between revisions of "Rn2"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(I don't think there's been any real changes to this...) |
(lede) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:rn2}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:rn2}} | ||
{{randomvariable|name=rn2(x)|graph=rn2.svg|caption=[[wikipedia:Probability mass function|Probability mass function]] of rn2(10).|distribution=[[Wikipedia:discrete uniform distribution|uniform]]|mean=<math>(x-1)/2</math>|stddev=<math>\sqrt{(x^2-1)/12}</math>}} | {{randomvariable|name=rn2(x)|graph=rn2.svg|caption=[[wikipedia:Probability mass function|Probability mass function]] of rn2(10).|distribution=[[Wikipedia:discrete uniform distribution|uniform]]|mean=<math>(x-1)/2</math>|stddev=<math>\sqrt{(x^2-1)/12}</math>}} | ||
| − | rn2(x) | + | '''rn2(x)''' is a pseudo-random number function used in the code of ''[[NetHack]]''. The function's purpose is to provide an "unweighted": the range of values is between 0 and x-1 inclusive (that is, 0 ≤ rn2(x) < x).<ref>{{function|rnd.c|rn2}}</ref> |
For example, to simulate a percentage chance: | For example, to simulate a percentage chance: | ||
Latest revision as of 08:15, 27 October 2022
| rn2(x) | |
|---|---|
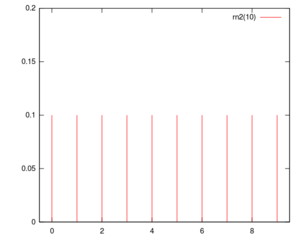 Probability mass function of rn2(10). | |
| Distribution | uniform |
| Mean | 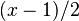
|
| Standard deviation | 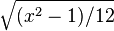
|
rn2(x) is a pseudo-random number function used in the code of NetHack. The function's purpose is to provide an "unweighted": the range of values is between 0 and x-1 inclusive (that is, 0 ≤ rn2(x) < x).[1]
For example, to simulate a percentage chance:
if (rn2(100) < chance) { ... }
Also,
!rn2(x)
is true with a 1/x probability.
See also rn1.